By Jhon Adrián Cerón-Guzmán et al
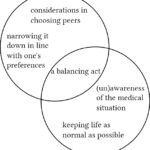
- Our findings reveal the preponderance of the lifestyle profile in locating peers.
- Seeking normalcy, individuals may favor suggestions from peers with similar lifestyles.
- Peer recommendations, enabling user control and potentially reducing search efforts, were favored.
- Design should attend to the everyday self-care strategies community members can contribute.
Users of online health communities have difficulty finding others with similar health experiences. They are often asked to use keywords when searching for their peers, but it is not uncommon for them not to know the right terms. This becomes particularly complex when unsure what or whom they are looking for. Moreover, the richness of patient perspectives is lost in the volume of discussion threads. In this paper, we investigate how to design to facilitate locating peers and learning self-care ideas from them. We created a prototype mimicking a mobile application for an online health community. The application recommended other community members to connect with and suggested self-care ideas based on what they had tried. Following a user-centered qualitative evaluation, we explore what ten people with cardiovascular disease and three clinicians thought of the prototype. Our findings reveal the preponderance of the lifestyle profile in locating peers. In light of this, we argue that, as individuals seek to lead as normal a life as possible, the most helpful suggestions in their quest may come from peers most similar to them in terms of habits and activity level. We translate the research findings into recommendations to inform future design.